Chlorine, Bromine, CFC, Carbon-Tetra-Chloride, Halons, etc.
Potential Drivers of Ozone Hole Over Antarctica :-
Changes in Antarctic polar vertex.
AdvertisementChanges in solar cycle
Increase in atmospheric abundance of chloro-fluro-carbons (CFCs)
Polar Vertex :-
Stratospheric wind patterns with vast low-pressure areas and very cold air, more pronounced over the south poles.
Leads to formation of polar stratosphere clouds (PSCs)
Impact of volcanic eruptions on ozone layer :-
Triggers massive stratosphere water vapor plume.
Injects large quantities of sulphur dioxide.
Contributes atmospheric bromine and hydrogen chloride.
Eruption particles provide surfaces for chemical reactions for ODS.
Polar Stratospheric Clouds :-
This is also known as nacreous clouds or mother of pearl
Formed below minus seventy eight (-78 degree celsius) and trap outgoing longwave radiation.
Location :-
Hunga Tonga Hunga Ha’apai, a submarine volcano in the Tongan archipelago located in the southern pacific ocean, erupted in January 2022.
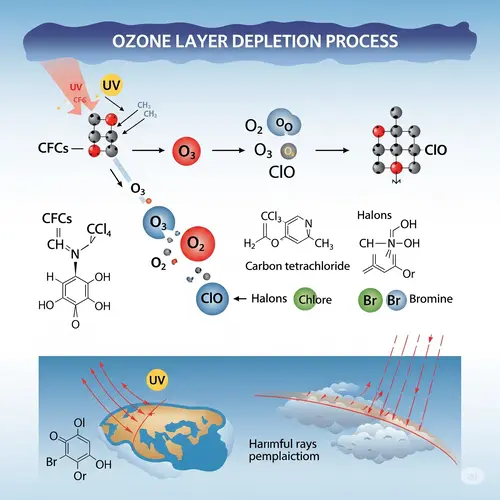
Ozone Layer Depletion Process (infographic) :-
UV rays split chlorine atom from CFC molecule.
Chlorine atom breaks up ozone molecule.
The chlorine molecule left behind creates chlorine monoxide and oxygen (O2).